Which gas is the best?
Choosing the most suitable gas depends on the specific application you require. Below is a comprehensive list highlighting the best uses for each gas that we offer:
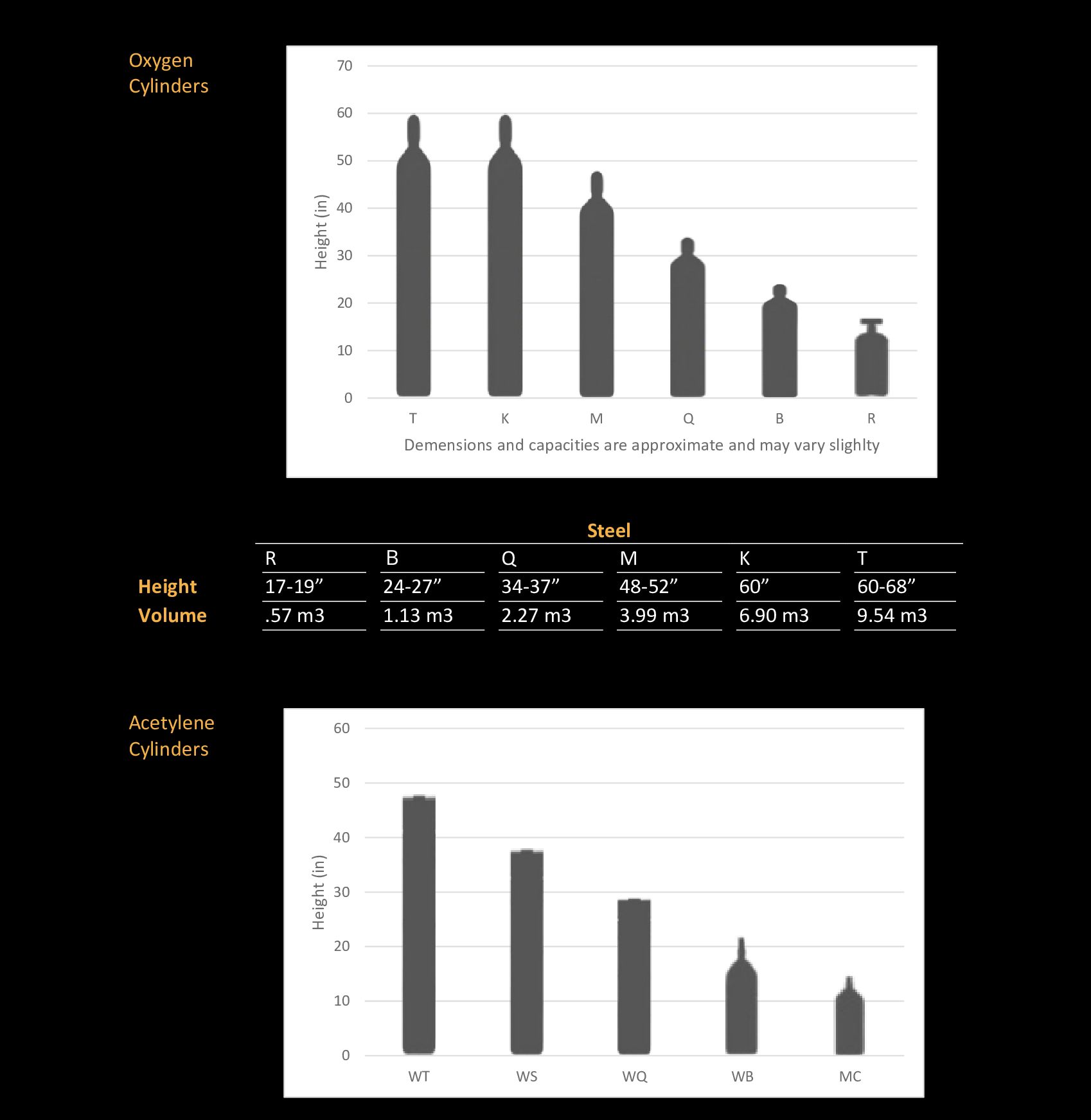
Oxygen: Oxygen is an incredibly versatile gas, primarily utilized in oxy-fuel welding and cutting processes. It plays a pivotal role in the oxy-acetylene welding and cutting of both ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Acetylene: Acetylene is extensively employed in various oxy-fuel welding, cutting, and heating applications. Renowned for its significantly high flame temperature, it is the preferred choice for cutting and welding thick metals.
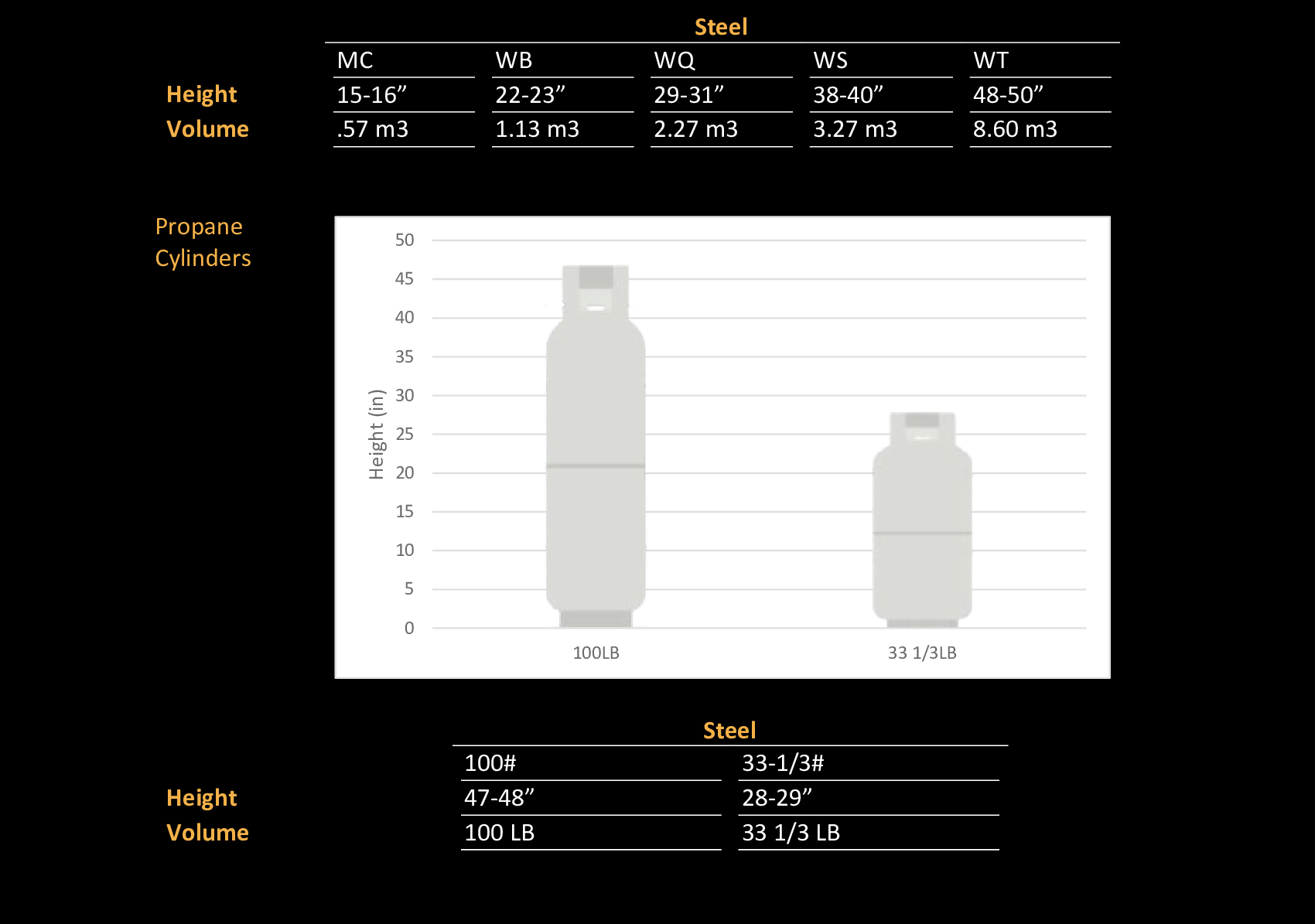
Propane: Propane serves a diverse array of heating purposes, ranging from soldering and brazing to flame cutting. It also functions as a reliable fuel gas for oxy-propane cutting and welding processes.
Argon: Argon is commonly used as a shielding gas in gas metal arc welding (GMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), and plasma cutting. It provides an inert atmosphere, preventing atmospheric contamination of the weld area, and is particularly suitable for welding reactive metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium.
Argon Mixes: Argon mixes, such as argon-carbon dioxide blends, are often preferred for their enhanced arc stability and penetration characteristics. They find extensive use in MIG welding applications, particularly for mild steel and stainless steel welding.
Helium: Helium is prized for its high thermal conductivity, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring high heat input, such as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) on thick materials or when deep penetration is necessary. It also finds use in various non-welding applications, including leak detection and pressurizing gas for purging.
Nitrogen: Nitrogen is commonly utilized as a purge gas in welding applications to prevent oxidation and ensure a clean weld zone, particularly in stainless steel and titanium welding. It is also used in laser cutting and as a pressurizing gas in some industrial processes.
Understanding the distinct roles and characteristics of these gases is essential in ensuring the optimal choice for your specific welding and cutting needs. Please feel free to reach out to us for any further guidance or information.